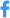
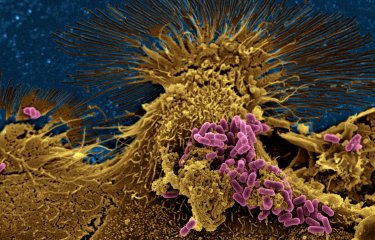
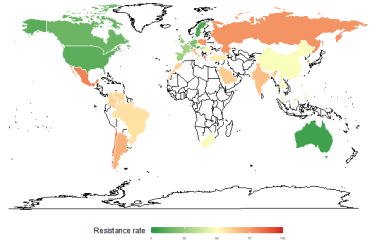
Scientists from twelve countries have recently joined forces to develop a program to identify new antimicrobial molecules. The project is based around the IRAADD, an international cooperation network of which the Institut Pasteur is a member.
Antimicrobial resistance remains a major public health issue with repercussions for several infectious diseases. Research on this issue is one of the Institut Pasteur's priority research areas, as laid down in its 2019-2023 Strategic Plan. Scientists from the Institut Pasteur recently contributed to a "roadmap" publication in the journal Nature Reviews Chemistry. The article provides a general overview of the current situation and proposes a research program to tackle the problem of antimicrobial resistance. The program is based around the IRAADD, the International Research Alliance for Antibiotic Discovery and Development, of which the Institut Pasteur is a member.
A network for translational science
IRAADD is an international network of scientists and industry partners that was set up to develop new antibiotic drug candidates. It has proposed a research plan to discover and develop molecules capable of overcoming the multidrug resistance witnessed in some infectious bacterial agents. To achieve these aims, the publication pleads the case for the development of translational science, which bridges the gap between basic research and industrial applications.
The roadmap emphasizes how important it is for skills, knowledge and individuals to be able to move freely between these two worlds. It also suggests that simpler legal frameworks are needed to manage the intellectual property of any new molecules developed as a result of complex collaborations between several organizations. Joining forces within a network is a way of raising awareness of the need for antibacterial drugs, finding sources of funding and communicating with decision-makers. The research paper, produced following a seminar attended by scientists and industry stakeholders, was signed by 54 authors from 12 different countries. The publication calls for further conferences and dedicated discussions to underpin these collaborations.
This study is part of the priority scientific area Antimicrobial Resistance of the Institut Pasteur's strategic plan for 2019-2023.
Source:
Towards the sustainable discovery and development of new antibiotics, Nature Reviews Chemistry, August 19, 2021
Marcus Miethke, Marco Pieroni, Tilmann Weber, Mark Brönstrup, Peter Hammann, Ludovic Halby, Paola B. Arimondo, Philippe Glaser, Bertrand Aigle, Helge B. Bode, Rui Moreira, Yanyan Li, Andriy Luzhetskyy, Marnix H. Medema, Jean-Luc Pernodet, Marc Stadler, José Rubén Tormo, Olga Genilloud, Andrew W. Truman, Kira J. Weissman, Eriko Takano, Stefano Sabatini, Evi Stegmann, Heike Brötz-Oesterhelt, Wolfgang Wohlleben, Myriam Seemann, Martin Empting, Anna K. H. Hirsch, Brigitta Loretz, Claus-Michael Lehr, Alexander Titz , Jennifer Herrmann, Timo Jaeger, Silke Alt, Thomas Hesterkamp, Mathias Winterhalter, Andrea Schiefer, Kenneth Pfarr, Achim Hoerauf, Heather Graz, Michael Graz, Mika Lindvall, Savithri Ramurthy, Anders Karlén, Maarten van Dongen, Hrvoje Petkovic, Andreas Keller, Frédéric Peyrane, Stefano Donadio, Laurent Fraisse, Laura J. V. Piddock, Ian H. Gilbert, Heinz E. Moser et Rolf Müller