Researchers at the Institut Pasteur and the French National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS) have just discovered the origin of hematopoietic stem cells (HSC), which give rise to all blood and immune cells in the body. Using real-time imaging technology on zebrafish embryos, the researchers observed that these stem cells were formed from the cells of the aortic wall, the embryo's main artery. This research, which has been published in the science journal Nature, though still at a fairly fundamental level, suggests that it might be possible to generate human HSCs in the laboratory using tissue samples from the blood vessels. This would open the prospect ofa personalized treatment for patients with leukemia, since their HSCs have to be replaced after chemotherapy or radiotherapy treatment to restore healthy blood and immune systems.
Press release
Paris, febuary 15, 2010
Two researchers at the Institut Pasteur and the CNRS working in the Institut Pasteur Macrophages and Development of Immunity Unit have just proved that hematopoietic stem cells, which produce blood cells throughout the life of each individual, are formed from the cells of the embryo’s aortic wall. The researchers used a high-resolution imaging technique to watch in real time how the aorta develops in zebrafish, a prime model for studying how blood cells are formed (a process known as hematopoiesis), enabling them to give an accurate description of the different stages in the birth of stem cells. This allowed them to answer the question of how blood stem cells come into being, a question which researchers have been trying to answer for many decades.
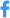
The observations show that some endothelial cells which make up the aorta undergo a strong bending outward, then fold upon themselves and round up to detach from the vascular wall, while still maintaining the integrity of the aorta. Each endothelial cell then becomes a free “travelling” stem cell which will divide so as to eventually give rise to all the different types of blood cells.
This discovery shows that cells that are already specialized, such as those which make up a blood vessel, can naturally re-program themselves to become multipotent stem cells.
Despite being still largely fundamental, this research opens the prospect of targeted treatments, particularly for leukemia patients, whose HSCs are destroyed by radiotherapy or chemotherapy. Once the factors driving this “dedifferentiation” have been identified, it might then be a matter of simply using a tissue sample taken from the patient’s own blood vessels to generate hematopoietic stem cells in vitro in the laboratory. Thesenew, custom-made HSCs could then be introduced into the patient to replace the old ones and restore the blood and immune systems.
- -
Formation of a stem cell from the aorta of a zebrafish embryo © Nature publishing goup.
Source
Blood stem cells emerge from aortic endothelium by a novel type of cell transition, Nature, online February 14, 2010.
Karima Kissa & Philippe Herbomel
Institut Pasteur, Macrophages and Development of Immunity Unit, CNRS Associated Research Unit URA2578.
Press contacts
Institut Pasteur Press Office
Nadine Peyrolo - Marion Doucet - + 33 (0)1 45 68 89 28 - presse@pasteur.fr